
What is the Best Unflavored Electrolyte Powder?
Experience Fast Hydration with – The Best Unflavored Electrolyte Powder – Boulder Salt You’re looking for the highest quality unflavored electrolyte

We’ve all heard before that we need more electrolytes in our diet or that, after exercise, we need to replace our electrolytes. But what are electrolytes? What do electrolytes do? And how can we get more electrolytes?
Simply put, an electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in water. The body needs electrolytes to survive, because the entire body runs on electricity: your brain works off of firing electric signals, your muscles activate because of electrical signals–everything about your body hinges on electricity being able to flow freely and naturally through the body. And while we’re not talking about plugging yourself into the wall, we are talking about making your body a better conductor for electricity.
Some of the most common electrolytes are sodium, potassium, calcium and bicarbonate, but also magnesium, chloride, and phosphate. Different electrolytes help the body in different ways: for example, your muscles rely on calcium, sodium and potassium to be able to contract.
The level of electrolytes can be too high or too low, which leads to an imbalance. And because electrolytes perform such an important function for the body, making sure that you’re perfectly in balance is important.
During exercise you lose essential electrolytes, especially sodium and potassium. Electrolytes can also go out of balance after the sudden loss of bodily fluids, such as through diarrhea or vomiting.
Symptoms of an electrolyte imbalance include: irregular heartbeat, weakness, twitching, sudden changes to blood pressure, confusion, numbness, fatigue, or even convulsions, seizures and nervous system disorders.
There are the obvious things that you hear about all the time, including exercise and dehydration, but more serious problems can also lead to imbalances, such as kidney disease, congestive heart failure, and simply aging kidneys. Poor diet can also cause problems, as can eating disorders, such as bulimia.
If you know the cause of your electrolyte imbalance – for example, if you have been doing heavy exercise – you can know that it’s time to replenish your electrolytes. But if you’re suffering from some of the symptoms listed above and don’t know the cause, lab tests can be done to measure your electrolyte levels. In the cases of serious causes, such as kidney disease and congestive heart failure, your doctor will help you manage your electrolytes.
But if you’re suffering from electrolyte imbalance because of dehydration – because of severe diarrhea, for example – the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the following oral rehydration therapy:
This mixture is to be dissolved in one liter of water and drunk in small sips. Warning…this mixture of salts tastes really bad.
Replace electrolytes naturally with the following foods:
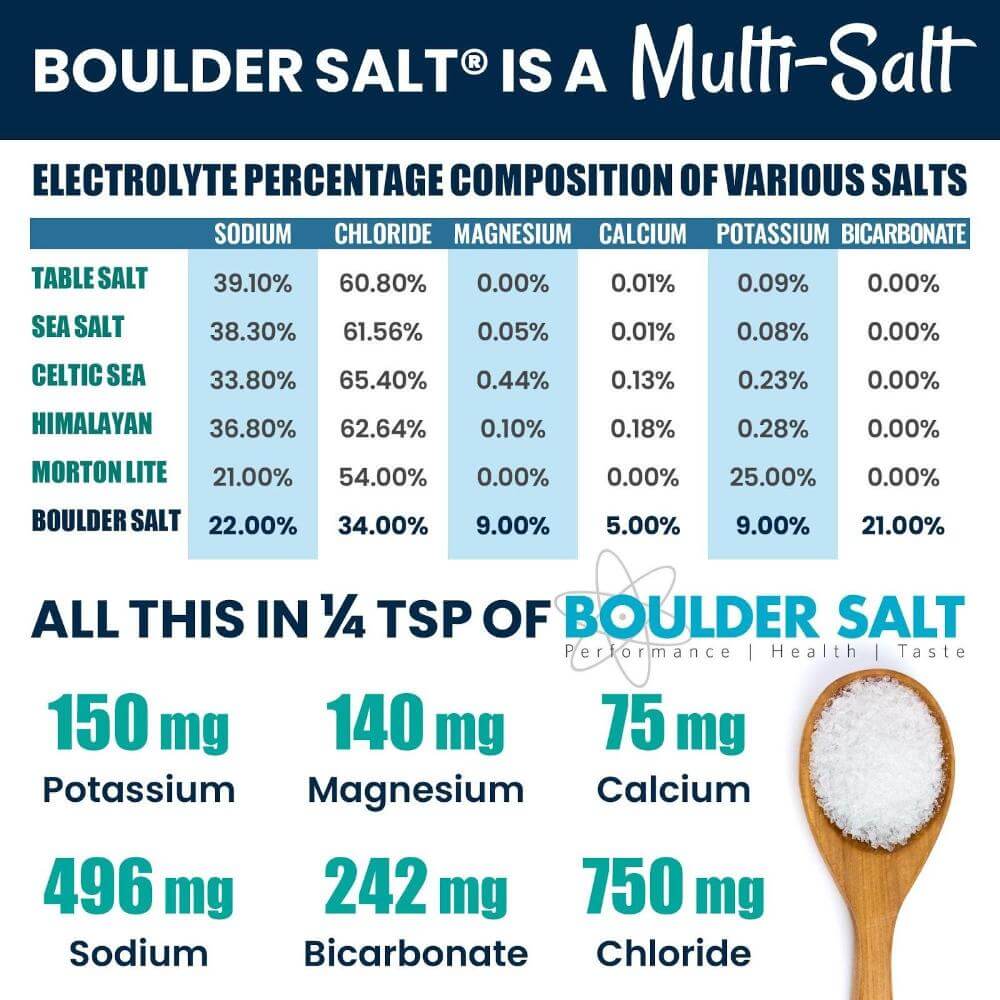
As you can see from the chart above, Boulder Salt contains all five of the primary electrolytes. You often hear that the secret to a healthy diet is to remove all the sodium from your food, and that’s not true. The secret is to get a balanced salt that replaces all of the recommended electrolytes.
This is why Boulder Salt is such a good alternative to table salt: it includes all of these electrolytes, but does so with 40% less sodium than table salt. You get enough sodium, but not too much, plus you get all of the other essential minerals.
More to explore

What is the Best Unflavored Electrolyte Powder?
Experience Fast Hydration with – The Best Unflavored Electrolyte Powder – Boulder Salt You’re looking for the highest quality unflavored electrolyte

Potassium-Magnesium Enriched Salt Substitutes for High Blood Pressure | Boulder Salt Company
Looking to shake up your salt game? Enter potassium magnesium enriched salt substitutes. These flavor enhancers offer a low-sodium alternative with the

Healthiest Salt? Is all salt built the same? The answer is no. Healthy salt with a high mineral content is crucial